Polyurethane foam spray insulation offers several advantages over other insulation materials. While there are many types of insulation and each has its pros and cons, polyurethane foam continues to gain traction in both the commercial and residential construction industry. In fact, the spray foam insulation market is forecasts significant growth between 2025-2034.
Spray Foam Insulation Stands Out as the Superior Product

Polyurethane foam spraying has revolutionized the insulation industry by providing a superior, versatile, and durable solution that enhances energy efficiency, structural integrity, and indoor comfort while offering significant long-term cost savings and environmental benefits. It is applied using a plural component proportioner and spray guns which deliver a properly mixed and consistent application of foam.
Learn the advantages of Polyurethane Foam Insulation
1. Superior Insulation Properties
Higher R-Value: One of the advantages of polyurethane spray foam insulation is that it provides a higher R-value per inch compared to traditional materials like fiberglass and cellulose. This results in better thermal performance and greater energy efficiency.
Air Sealing: Polyurethane foam expands upon application, filling gaps, cracks, and crevices to create an airtight seal. This drastically reduces air leakage, which is a common issue with other types of insulation.
2. Moisture Control and Durability
Moisture Barrier: Many spray foam formulations can act as an effective moisture barrier, preventing water infiltration and reducing the risk of mold and mildew growth when applied correctly. This is especially important in areas prone to high humidity or water intrusion.
Longevity: Polyurethane foam is highly durable and maintains its insulating properties over time, unlike some traditional insulations that can degrade, settle, or lose effectiveness.
3. Structural Integrity
Enhanced Structural Strength: Closed-cell spray foam adds rigidity and strength to walls and roofs due to its dense and hard structure. This can improve the overall structural integrity of buildings.
4. Versatility and Flexibility
Adaptability: Polyurethane spray foam can be applied to a variety of surfaces and in hard-to-reach areas, making it suitable for both new construction and retrofit projects. Its flexibility allows it to be used in unconventional spaces where traditional insulation might be impractical. PMC Hoses can reach lengths of 410 feet, or more with the auxiliary hose heat system.
Custom Application: The ability to control the thickness and density during application allows for customized insulation solutions tailored to specific needs, climate zones, and building requirements.
5. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
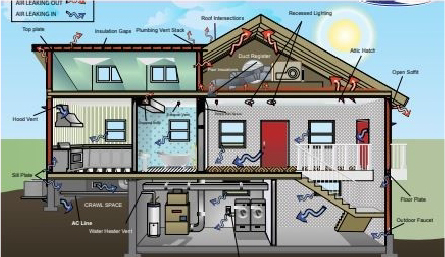
Reduced Energy Consumption: By providing superior thermal insulation and reducing air leaks, spray foam insulation can significantly lower heating and cooling costs. This results in substantial energy savings over the life of the building.
Return on Investment: Although the initial cost of spray foam insulation can be higher than traditional materials, the long-term energy savings and increased property value often provide a heavily favorable return on investment.
6. Environmental Impact
Reduced Carbon Footprint: The energy savings achieved through better insulation directly contribute to a lower carbon footprint. Additionally, some polyurethane foams are made with environmentally friendly blowing agents and recycled materials.
Sustainability: The durability and longevity of spray foam reduces the need for replacement and maintenance, leading to less material waste over time.
7. Health and Comfort
Improved Indoor Air Quality: By creating an airtight seal, spray foam insulation helps to prevent the infiltration of pollutants, allergens, and outdoor noise, contributing to a healthier and more comfortable indoor environment.
Temperature Regulation: The enhanced insulating properties help maintain consistent indoor temperatures, improving overall comfort for building occupants.
8. Time and Labor Efficiency
Faster Installation: Spray foam can be applied quickly and efficiently, reducing labor costs and construction time. This is particularly beneficial in large-scale projects or when retrofitting existing buildings.
One-Step Application: Unlike traditional insulation that may require separate vapor barriers or additional sealing measures, spray foam can provide insulation, air sealing, and moisture control in a single application.
Choosing the right type of insulation depends on various factors including climate, building structure, budget, and specific insulation needs. Polyurethane foam, particularly closed-cell spray foam, is often preferred for its superior insulating properties and versatility, but other materials may offer distinct advantages in different scenarios. Working with an experienced and knowledgeable contractor is key to making the right selection.
Other Types of Insulation Materials
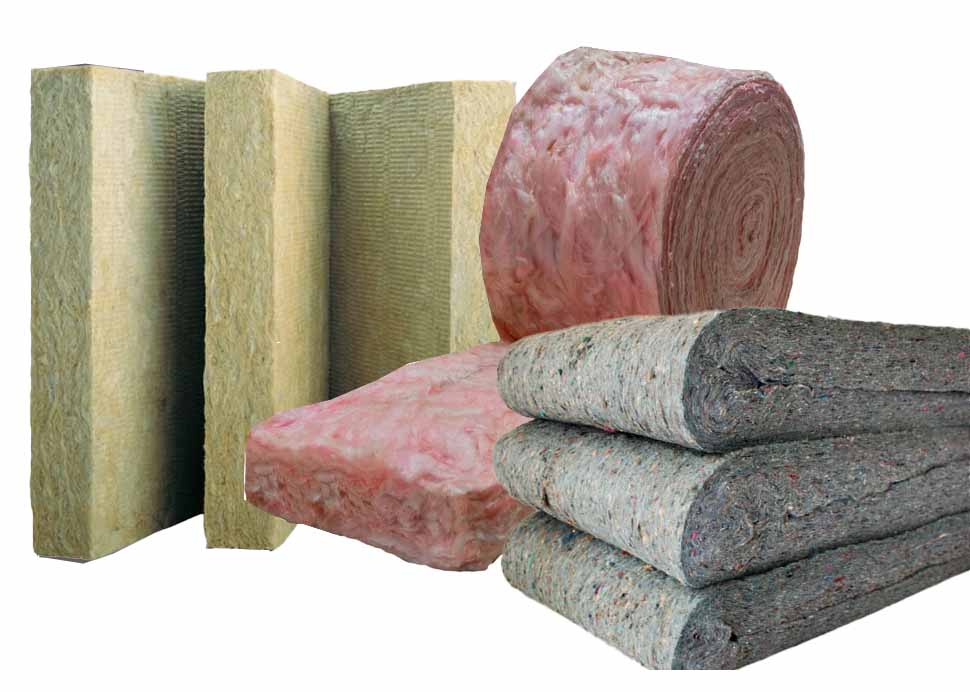

To fully understand the value of polyurethane spray foam, let’s explore the pros and cons of some alternate materials to determine the right choice for your construction project.
1. Fiberglass Insulation: Made from fine glass fibers and available as batts, rolls, or loose-fill.
– Pros: Cost-effective, widely available, easy to install.
– Cons: Can cause skin and respiratory irritation, lower R-value, prone to gaps and settling.
2. Cellulose Insulation: Made from recycled paper products and treated with fire retardants. Available as loose-fill or blown-in.
– Pros: Environmentally friendly, good thermal performance, better fit in irregular spaces.
– Cons: Can settle over time, potential for mold growth if exposed to moisture.
3. Mineral Wool Insulation: Made from rock or slag fibers. Available as batts or loose-fill.
– Pros: Fire-resistant, good soundproofing qualities, does not absorb water.
– Cons: Higher cost, heavier, can be irritating to handle.
4. Rigid Foam Insulation: Available in boards made from polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, or polyurethane.
– Pros: High R-value per inch, moisture-resistant, provides structural strength.
– Cons: Higher cost, requires careful installation to avoid gaps.
5. Reflective or Radiant Barrier Insulation: Made from reflective materials like aluminum foil, often used in attics.
– Pros: Effective in reducing heat gain in hot climates, easy to install.
– Cons: Less effective in cold climates, relies on air spaces to function properly.
Understanding that every situation is different, polyurethane spray foam insulation stands to be the best option for most commercial and residential applications. When looking for a spray foam contractor, be sure to ask about their experience and the equipment they use. PMC spray foam equipment, when used by knowledgeable contractors will get the job done with superior results every time.

